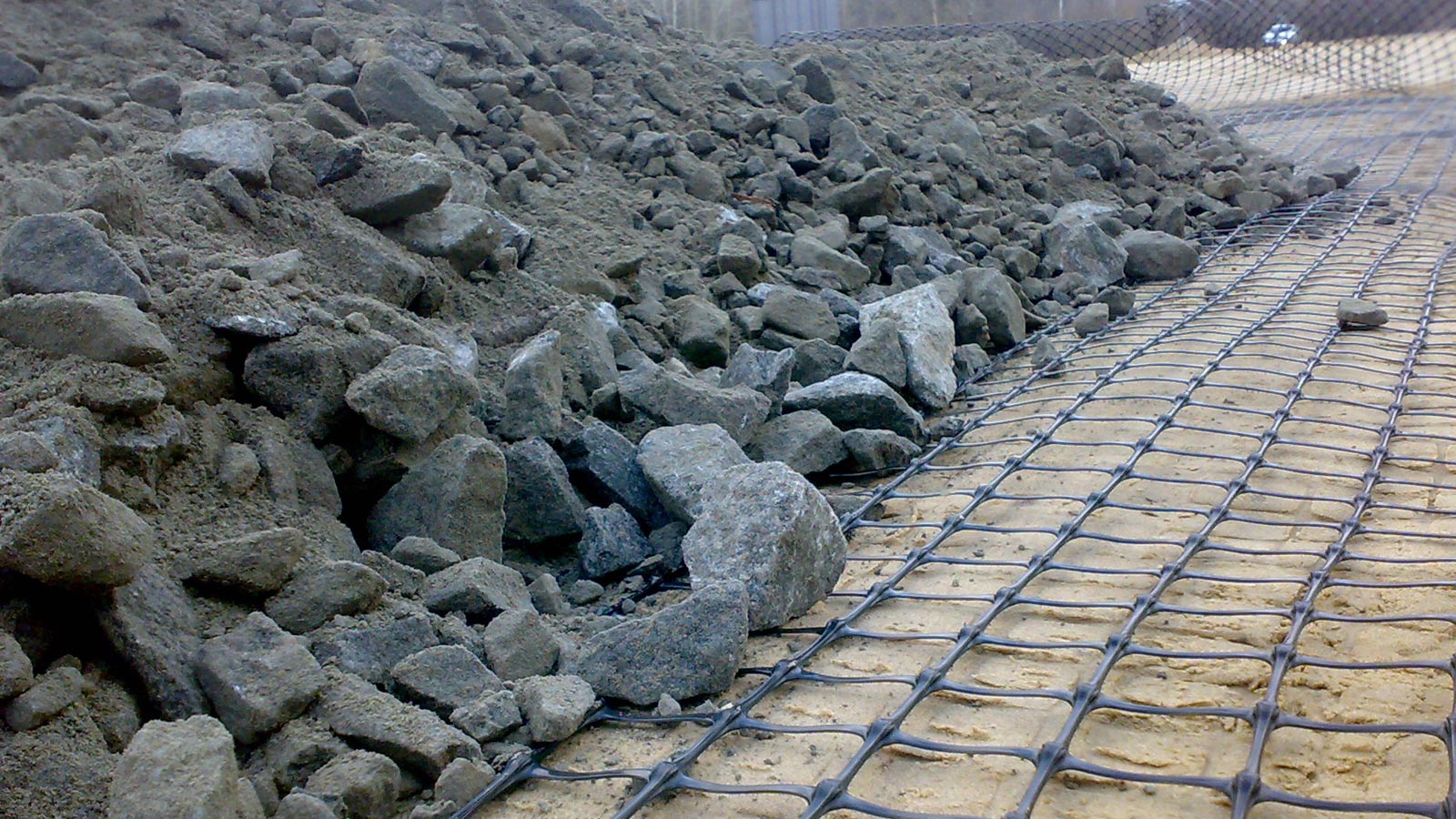
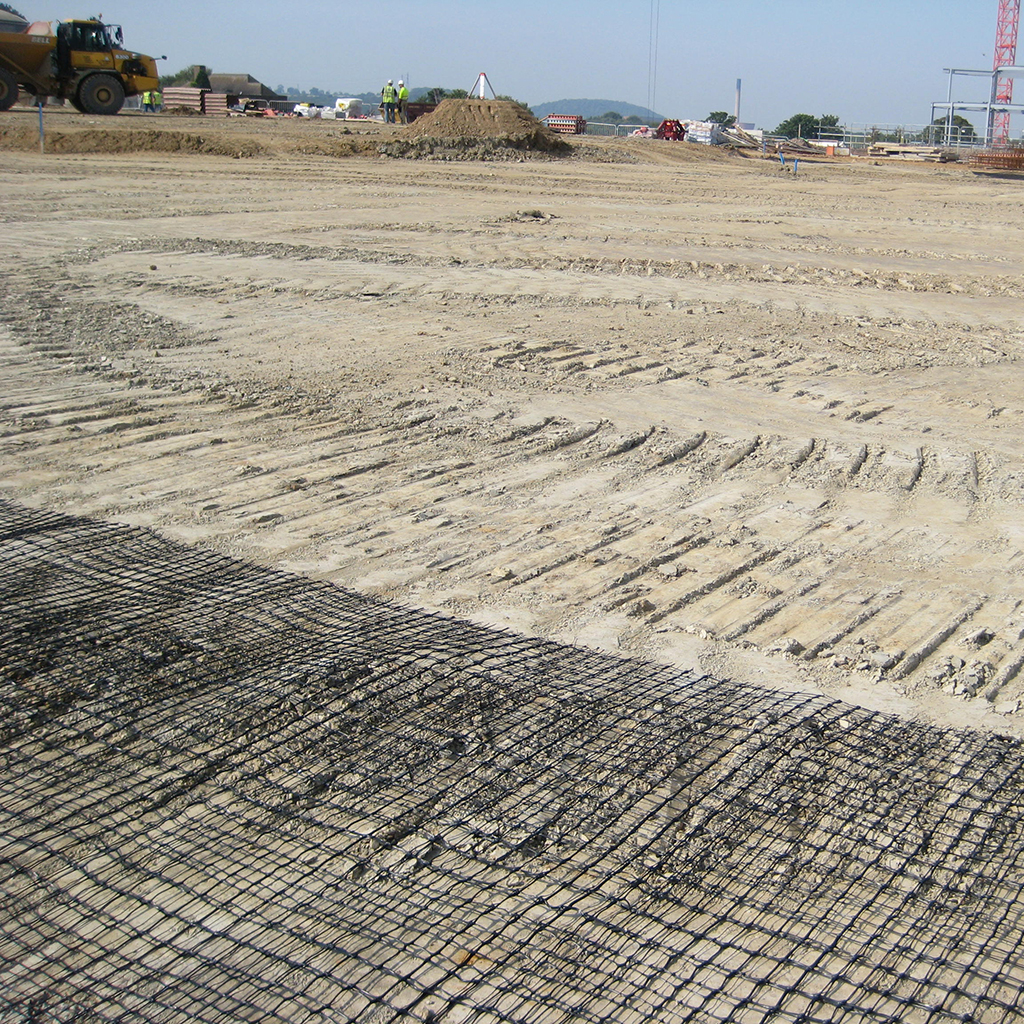
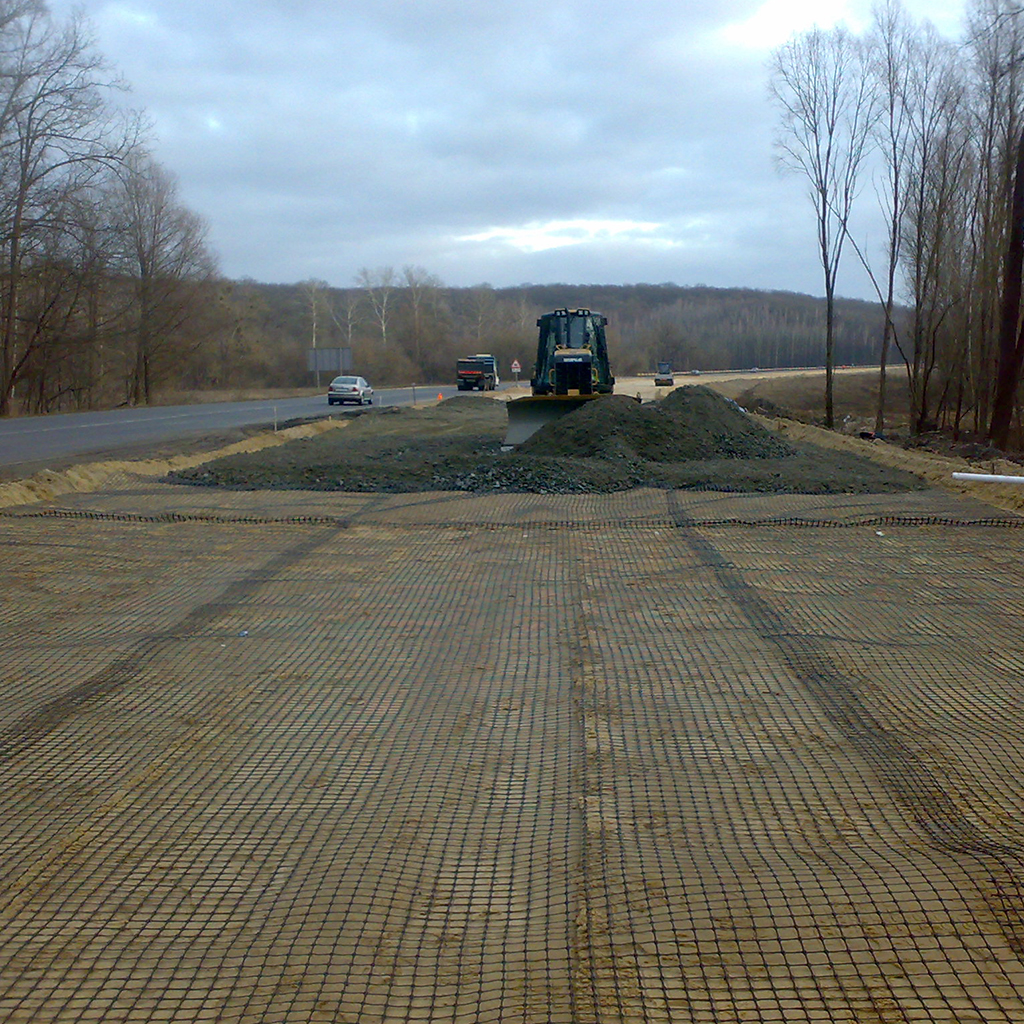
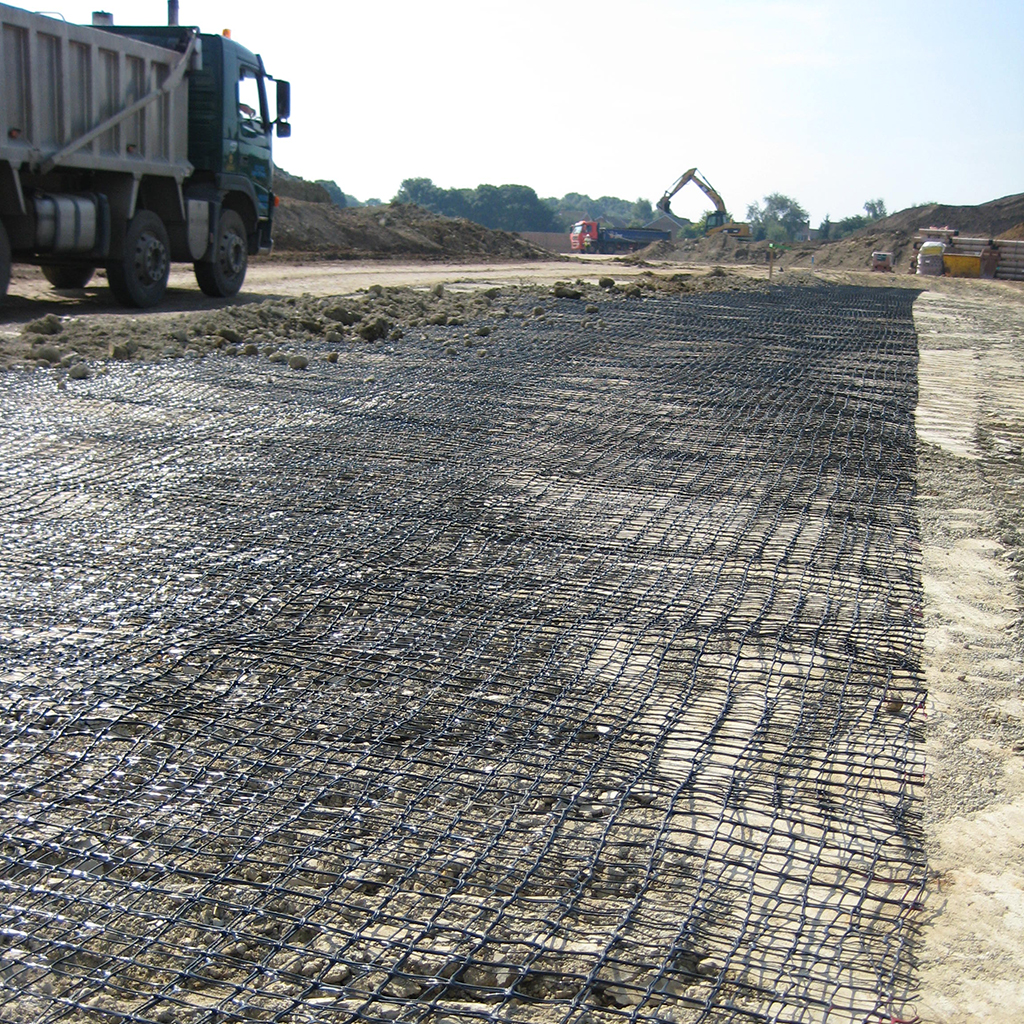
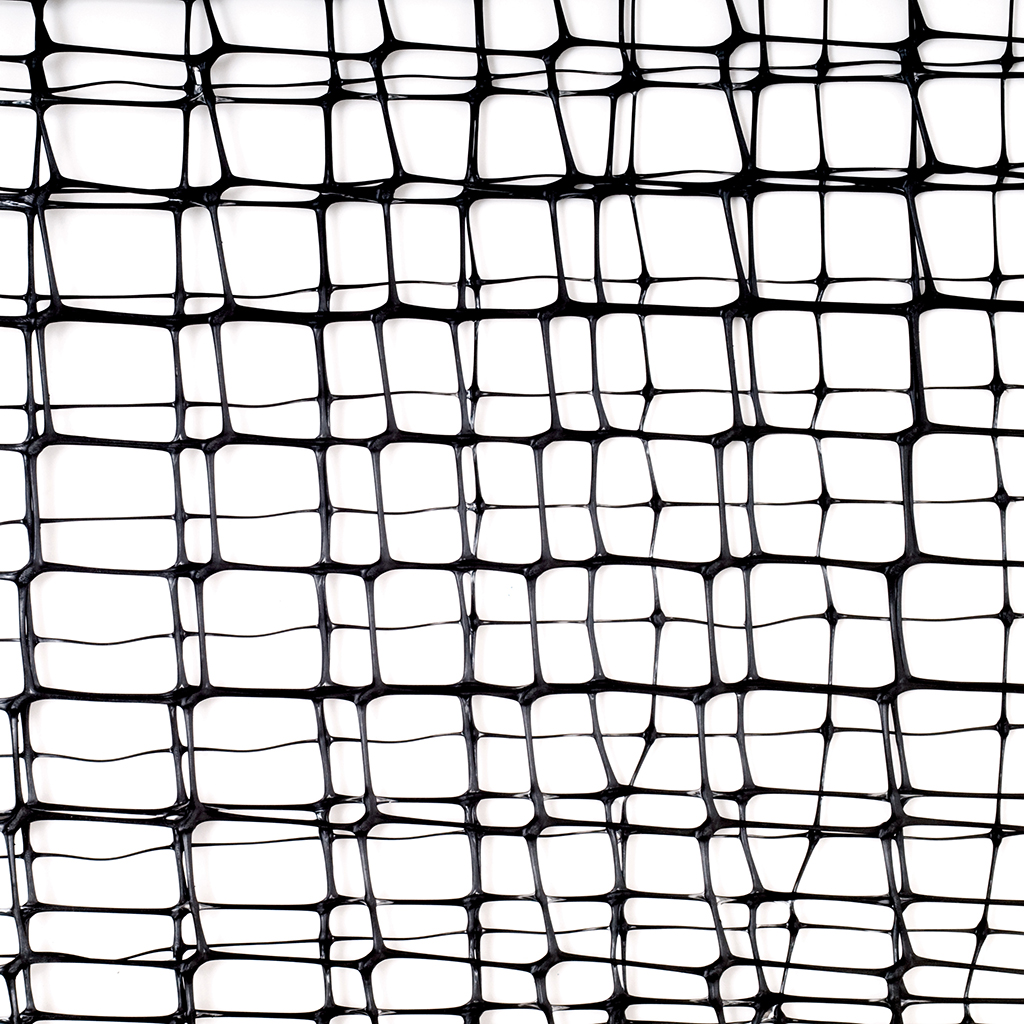
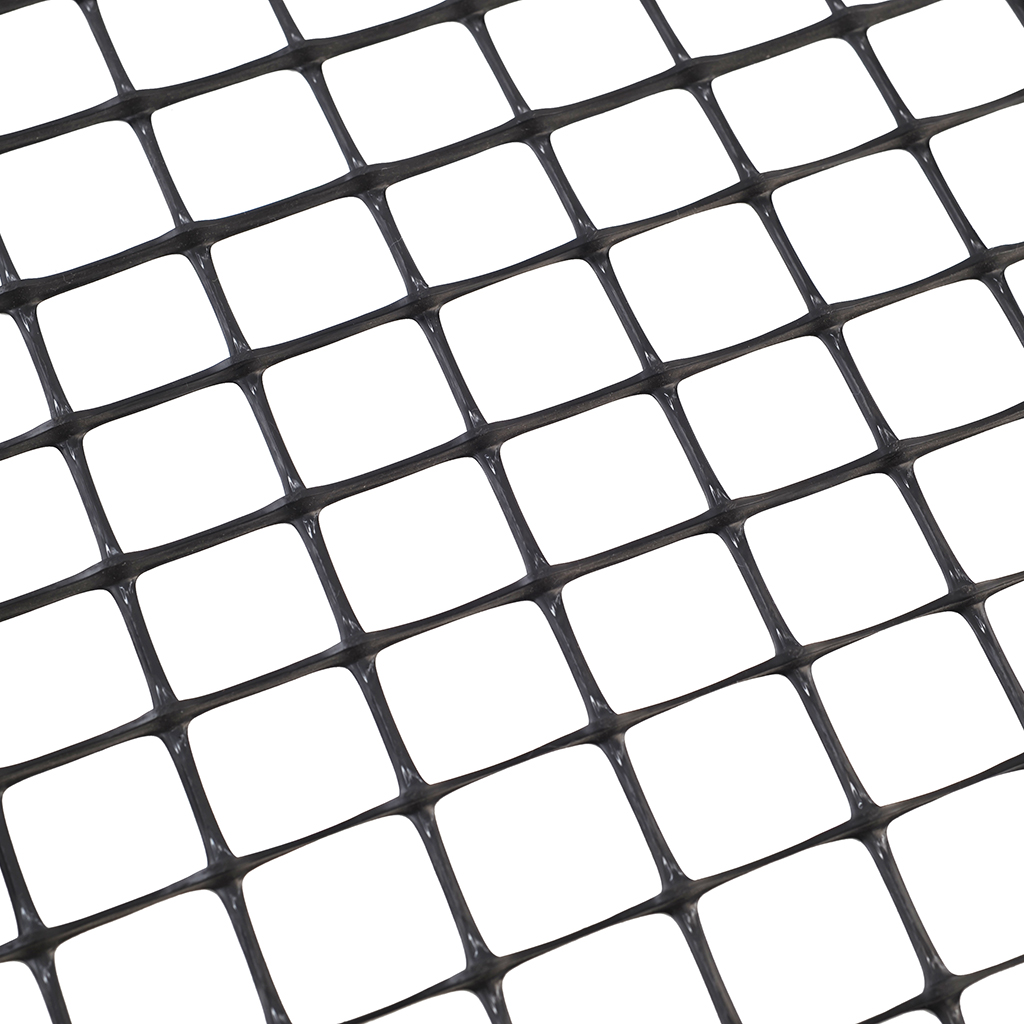
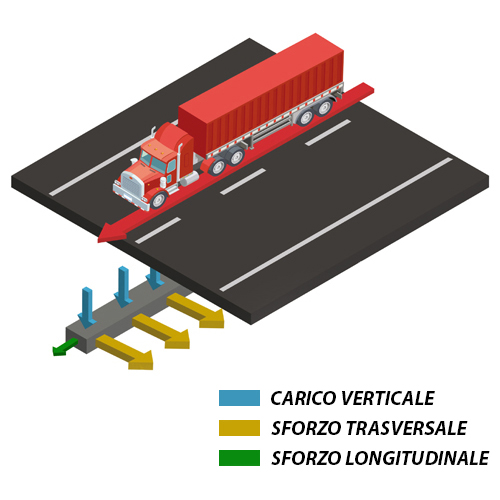
The innovative 3D GRID three-dimensional geogrids are specifically designed for road and railway applications, where the load applied to the ground develops mainly in the longitudinal direction of the structure. The 3D Grid three-dimensional geogrids represent a significant improvement over traditional geogrids: thanks to its technology, Tenax is able to offer geogrids with a true third dimension.
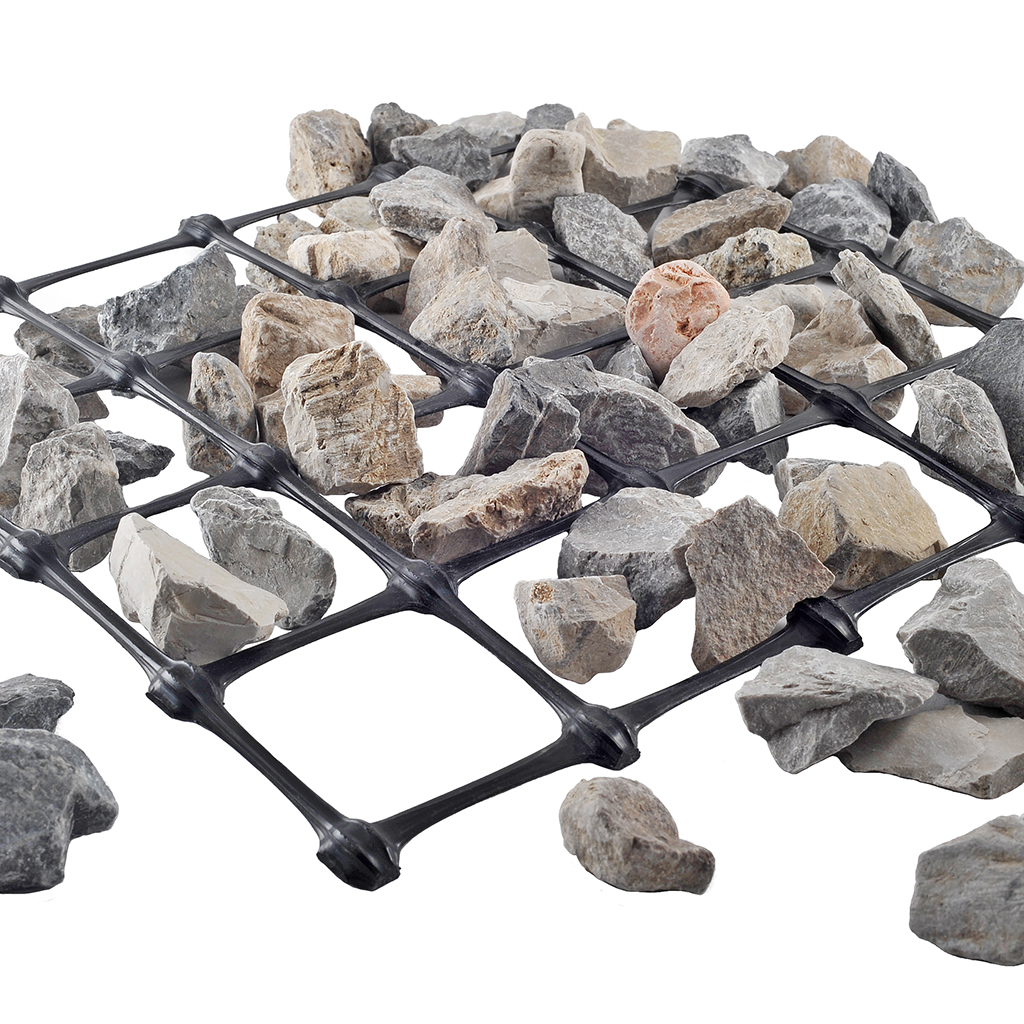
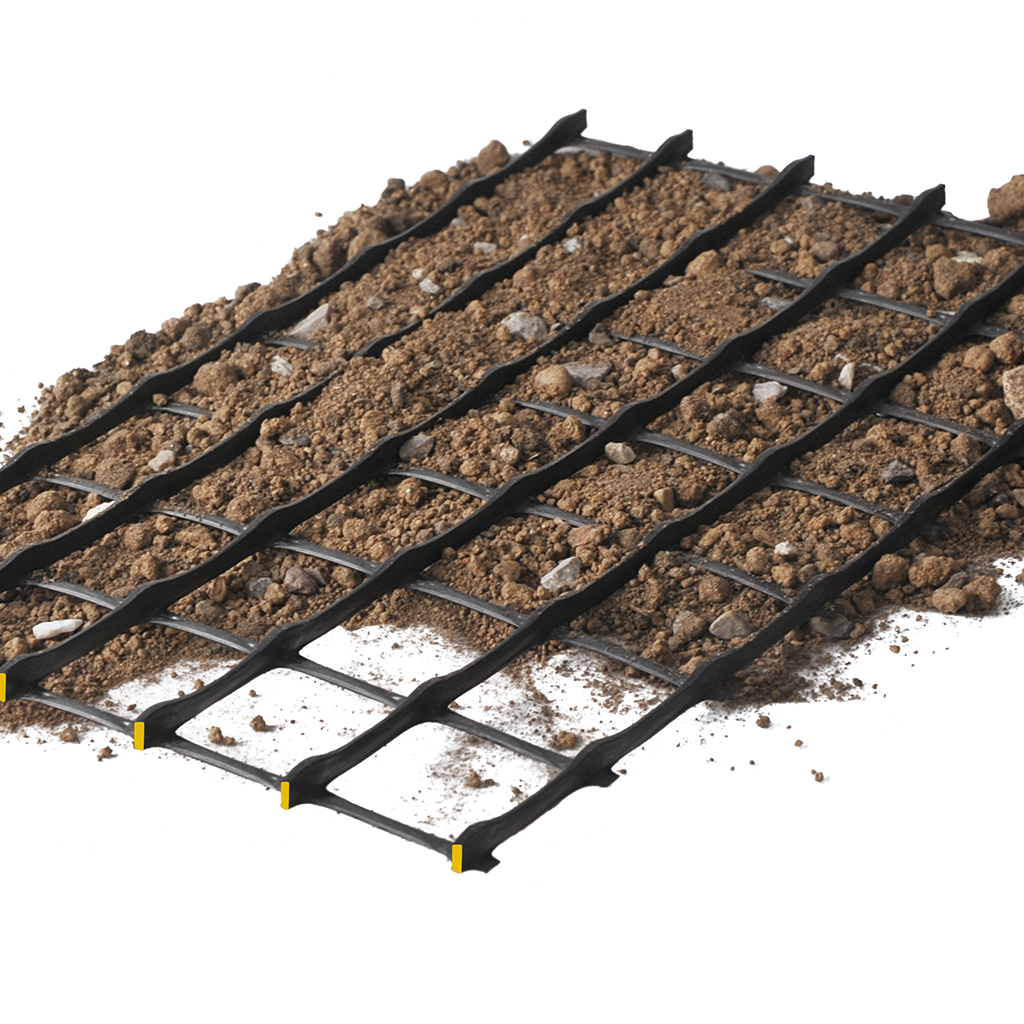
The thickness of the wires and knots creates a lateral confinement action, which, combined with a specific mesh for each type of soil, maximizes the interlocking between the soil and the geogrid. All this translates into superior performance that allows for better load distribution and, consequently, a reduction in the formation of potholes and ruts, as well as a decrease in the thickness of the base layer of roads and railways.
Tenax 3D Grid geogrids are available in two types: S and XL.
They differ in terms of structure, wire thickness, and mesh size so that they can be used in all types of soil.
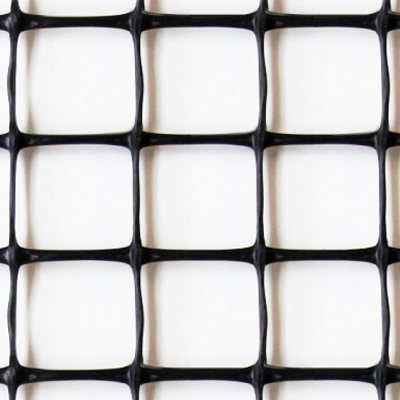
3D GRID S three-dimensional geogrids are made with thicker longitudinal wires and a 30 x 30 mm square mesh, making them ideal for reinforcing small to medium-sized soils.
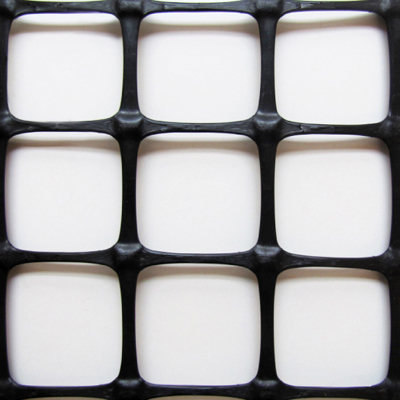
3D GRID XL three-dimensional geogrids are characterized by significant dimensions in all three main directions. The concave ribs with significant thickness and the size of the openings (60 x 55 mm) allow for optimal interaction with large-sized granular materials.